Keywords |
| Technology acceptance model (TAM); Assertive;
Aggressive; Passive |
Introduction |
| Over time, definition of bank as an organization taking deposits,
lending and helping customers in managing risk has been changed due
to time pressure and competition in global banking which has created
multifaceted group comprising of diverse products and services
operating across various business lines. The supreme modernization
in banking that has occurred due to the payment system which has
taken momentum in the developed world and also well accepted in
the budding market. The rapid penetration of mobile devices in the
cashless society has significant effects on every day activities of people.
Disruptive technology in context to mobile technology, provided
dynamics in delivering health services which has changed the societal
value and communication eco system. New horizons of life have been
integrated to societal well beings. The possession of cell phone by users
is more than PCs in India. The bankers are trying to take advantage of
these devices for distributing their banking and financial services. |
| In the present banking scenario in India, mobile banking
registration is increasing 50% more than the Internet banking as per
the data revealed by different private and public sector banks in India.
In comparisons to the internet transaction over mobile transactions
if growth of mobile banking sustain over a period of time it will
cross internet transaction. Banks are providing location based offers
for customers for getting notification through their iWatch and are
adding tag feature to introduce the concept of ‘tap and pay’ without
customer having to reach for his wallet. Mobile banking is an approach
for providing financial services through ICT. Mobile phones offer
the advantage of using financial services 24/7 at any place. It creates
a stronger relationship between banks and customers. Physicians are
providing mobile health services to patients, so that their work may
be better supported, and obtain useful information and guidance to
manage their health services better. |
| Despite the potential benefits of mobile healthcare services,
physicians have inevitably encountered numerous difficulties
and challenges in transacting their financial transaction through
mobile devices. The omnipresence and multifunctional core of these
devices along with their features allows mobile users to add different
applications to their mobile devices and customize them based on
preferences as well as use them to address their needs. Therefore,
factors that influence the adoption of mobile banking services by physicians must be investigated. The objective of this study is to analyze
the behavior style of physicians on the attitude towards the adoption
of mobile banking. In the research we tried to integrate behavioral
variables with TAM Model. |
Mobile Banking in India |
| As research report, by 2018, 130 million markets will be created by
Smart Wearable devices, and these will provide massive opportunities
to cash on by the Banks in delivering their banking transactions. Banks
in the future will be using smart watches and Google glass to create
a niche market for mobile banking. Internationally mobile banking
situation is favourable as evident from user adoption statistics across
all different regions. |
| In Australia,5 million mobile banking customers in 2013 Banks
reported that 60% of transactions were done using NFC contactless
payments in 2013, In Europe, 38% of the European mobile consumers
have adopted mobile banking Stable adoption rate 56% of the mobile
banking users are from Turkey and 38% from the UK. In, Asia, China
and India record the highest banking app users at 73% and 59%
respectively 19% banking app users in Japan indicates relatively slow
adoption of mobile banking. Chinese mobile transaction value was
around US$360 billion. |
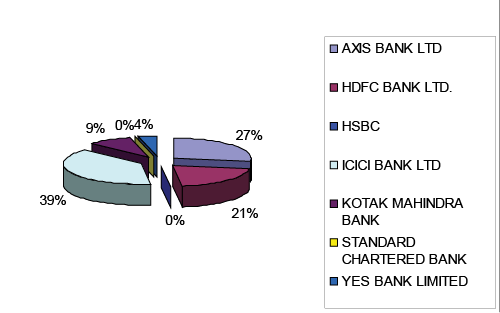
| Among private sector banks the leading top players are ICICI
Bank Ltd, Axis Bank followed by HDFC Bank Ltd in mobile banking
transaction in volume (actual to value in Rs.’000) (Figure 1,2) (Table
1,2). |
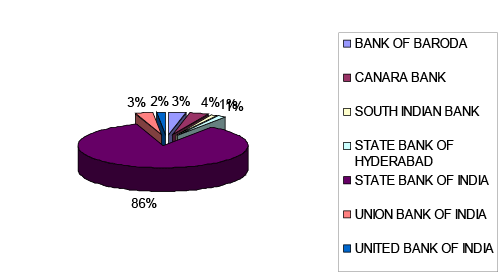
| Among public sector banks the leading top players are SBI, Canara
Bank followed by Union Bank of India in mobile banking transaction
in volume (actual to value in Rs.’000). |
| In comparison to Sep-2015 the volume (actual to Value (in Rs.000)
has been increased month wise which indicates there is trend towards
conduction banking transaction through mobile month by month
(Table 3,4). |
| Web transaction and mobile transaction seems to be comparable
which can surpass the internet transactions in future ahead. The growth
of the usage of mobile forces the banks to deliver their financial services
though these devices with the changes of dynamism of customer
expectation in conduction banking services. |
Literature Review |
| TAM (Technology Acceptance Model) traces its root from TRA
(Theory of Reasoned Action) to psychology to information system (IS)
and is widely used for studying the use and acceptance of technology.
As specified by Davis [1] the TAM model PEOU a PU is the key
variables for the determinant for the behavioral intention to use the
technology as argued by the model and has strong control on attitude.
The TAM model have been enriched by IDT (Innovation Diffusion
Theory) by different researchers. Different research conducted in
different countries in context to adoption of mobile banking applied
Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) Model, Theory of Planned Behaviour
(TPB), Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) model constructs. Lee
and Mattila discussed the importance of perceived risk on adoption
behavior and has found Jacoby and Kaplan’s six risk dimensions
applicable to adoption behavior in the Mobile banking context. |
| Behavioral intention is the main determinant of one’s actual
behaviour which is determined by attitude [2]. Legris critically
examined the external variables and found they are the drivers of
technology. Many researchers have explored the effect of external
variables on technology usage as well as relationship between individual
differences and acceptance of technology. Mattila found adopters
of mobile banking relatively young and majority of them belong to
25-34 years and non-adopters display different socio-demographic
characteristics. TAM uses perceived usefulness and perceived ease-ofuse
as key determinants to explain users’ acceptance of IT [3]. Adopters
are willing to use mobile banking when they perceive it to be useful
and helpful for the efficiency of their work. So PEOU, PU constructs
have a direct effect on behavioral intention. Adams [4], Agarwal [5],
Venkatesh [6] and Venkatesh [7] found a significant relationship
between individual differences and technology acceptance. Lee found
that innovative attributes are related to consumers’ attitudes toward
adoption. Mattila [8] pointed out availability of mobile services as an
important factor in the adoption of mobile banking. Nor [9] found
risk, trust, social norms, perceived usefulness, attitude, self-efficacy and
perceived ease of use are the key determinants in adoption of Internet
banking. |
| According to TRA, an individual’s behavioral intention, which
results in actual behavior, is influenced by his/her subject norm and
attitude, and the attitude is influenced by individual beliefs [10].
However, despite the growing interest in the field of mobile banking,
there has been limited empirical literature that explored the customers’
attitudes and intentions toward mobile banking in context to the
behavioral style with attitude formation. PEOU refers to the degree to
which a person believes that using a particular system would be free
of effort. Malhotra, Gefen and Matheison argued in their study PEOU
is one of the main variables influencing other variables on adoption
of technology Agarwal and Prasad [5], Davis [3] provided evidence of
PEOU having a significant effect on behavioral intention for adoption
of technology. |
| PU is defined as the degree to which a person believes that using a
particular technology will enhance his performance. Araujo, Noteberg,
Gefen, Matheison and Malhotra considered PU as an important
variable in TAM. Perceived Usefulness has been confirmed as an
important variable that influences user technology acceptance and
therefore has received a great deal of attention from prior researchers.
Davis [11] defined perceived usefulness as the individual’s perception
that using the new technology will enhance or improve her/ his
performance. Chau [12] in the study on understanding physician’s
usage of telemedicine adoption used the TAM model which explained
the telemedicine adoption. |
| Perceived usefulness was found to be the most significant
determinant of Behavioral intention to use and Attitude in the model.
Mathwick defined perceived usefulness as the extent to which a person
deems a particular system to boost his or her job performance. Agarwal
[13], Davis [3], Venkatesh [14,15]. TAM suggests that attitude is based
on the salient beliefs which a person has about the consequences of
a given behavior and his or her evaluation of those consequences.
Understanding the determinants of consumer’s attitude, it is argued
that this attitude has a strong, direct, and positive effect on customers. |
| Assertive behavior is usually honest, direct, expressive,
spontaneous, and self-enhancing. Assertive persons make their own
choices, are confident, and feel good about themselves while being
assertive and afterward. They usually achieve their goals; when they
don’t, they still feel good about themselves because they know they
have been straightforward. Assertive behaviors among the physicians
uphold personal self-respect and cultivate health relationship with
others. |
| Assertiveness describes having a positive attitude towards yourself,
and others. It is about being honest, respecting yourself and with
others. When you are self confident and your behavior is assertive, you
are open to others and their views event though they may be different
from your own. Your opinion, beliefs and feelings is important for you
as well as for others. Assertive behaviour is all about, being honest,
mutual equilibrium and benefit in a relation ship, getting more social
responsibility, and showing respect to others. |
| Passive behavior: The person who behaves non-assertively in
a situation does not assert his/her basic rights, instead he/she allows
others to disobey upon them. Passive Behavior includes not expressing
feelings, needs, and ideas; ignoring personal rights; and allowing others
to disobey upon them. |
| Nonassertive behavior is usually emotionally dishonest, indirect,
inhibited, and self-denying. Nonassertive persons often let other
people choose for them and end up feeling disappointed in themselves
and angry with them. |
| Aggressive behavior: The person who behaves
aggressively in a situation asserts his/her basic rights at the expense of
the other person’s rights. He/she does not respect that other person
has rights. |
Negative attitude and passive behaviour |
| • Low self esteem and Lack of self confidence. |
| • Lack of self respect |
| • Negative feelings and thoughts about yourself |
| • Feelings of inferiority compared to others |
| • Like others to be in control of people and situations |
| • Demotivated |
Negative attitude and aggressive behaviour |
| • Lack of self confidence and low self esteem |
| • Lack of respect towards others |
| • Put others down |
| • Feelings of superiority |
| • Don’t listen to or ask questions |
Positive attitude assertive behaviour |
| • Self confidence and high self esteem |
| • Respect for self and towards others |
| • Take responsibility for self |
| • Motivated to do a good job |
| • Interested in others’ feelings and thoughts |
| • Ask questions |
| • Honest and direct |
| • Listen to others |
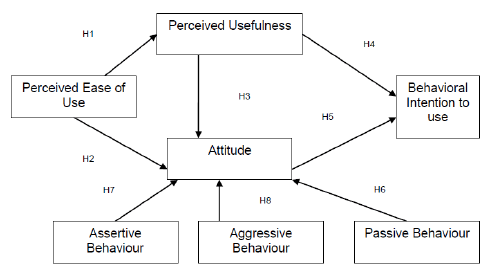
Research Model |
| The research model depicted below is an effort to consist of external
variables to effect the attitude formation. The model is specifically to
answer the following research question (Figure 3): |
| How TAM does related factors and different behavioral styles
impact the attitude. |
| H1: Physician’s Perceived Ease of Use has a positive significant
impact on perceived usefulness of mobile banking. |
| H2: Physician’s Perceived Ease of Use has a positive significant
impact on attitude towards using mobile banking. |
| H3: Physician’s Perceived Usefulness has a positive significant
impact on attitude towards using mobile banking. |
| H4: Physician’s Perceived Usefulness has a positive impact on
behavioral intention towards using mobile banking. |
| H5: Physician’s Attitude towards using Mobile banking has a
significant impact on behavioral intention to use it. |
| H6: Physician’s Passive behavior has a significant impact on
attitude towards mobile banking. |
| H7: Physician’s Assertive behavior has a significant impact on
attitude towards mobile banking. |
| H8: Physician’s Aggressive has a significant impact on attitude
towards mobile banking. |
Methodology |
Sampling and data collection |
| This study was conducted in three private medical colleges and one
public hospital consisting of health care professional’s i.e., physicians,
nurses and para medical staff located in the capital of Odisha, India. The
survey was confined to the physicians and the data was collected from
them. Systematic random sampling was used and had given a response
rate of 41% from the potential sample of 700. Practically around 92%
of the population of physicians are having a practical exposure to the
smart phones and are very well conversed with the devices. 85% are
familiar with the social media tools i.e., whatsapp and facebook and
using different apps for their online shopping and payment. Averagely
65% on an average are familiar with the personal computers, 45% of
them use their email daily i.e., confined to the physicians working in the
private hospitals. Physicians confined to private hospital in teaching are
using daily their personal computers for email and other search engine
for searching their medical information. 10% of the physicians use their
social media for communicating with the patients through mobile.
Physicians were asked to rate their knowledge of using electronic
health care system or telemedicine system or online consulting on a
scale of from 0 to 5, none to expert. Mean value of 1.28 is obtained
indicating physicians are having poor knowledge or very less exposure
to the online consulting or remote health care system. Physician in
private hospital have more exposure to the electronic health system
than the physicians working in public hospitals. Demographically,
majority of the respondents were male (73%) and female (27%) with
a mean age of 49 years. The sampling frame was compared with other
state in India which indicated representation of distribution of sex, age
and specialization is well justified which indicates sample is a proper
representation of the population. |
Variables and measures |
| Five-point Likert scale from 1 = “Strongly Disagree” to 5 = “Strongly
Agree” was used for measuring the items. Items used are adopted
from sales validated by previous researchers in context to adoption of
mobile banking in different countries, thus leading to the validation
through content validity. TAM scale items were adopted from Davis
[3], Chau [12] and Venkatesh [6]. Factor analysis using SPSS statistical
software was used to test reliability and to test hypotheses. Cronbach’s
alpha values were used to test the reliability of the measurement scale
adopted for the study. The reliability coefficients for all the predictors
are above 7 [16]. Principal Component analysis was employed for the
factor analysis. Factor loading of .5 are taken into consideration which
are very significant in this study [16]. |
Result measurement model analysis |
| Hypotheses based on SEM were tested using PLS multivariate technique (partial least squares) approach. This evaluate both structural
and measurement model. Smart PLS software with bootstrapping
method was used to analyse the data. Average variance extracted was
greater than .5. Structural model depict the causal relationship among
the constructs, path coefficients and the R2 value. Path coefficients and
R2 indicate how well the data support the hypothesized model. PLS
(Partial Least Square is used to evaluate the model. It assesses reliability
and validity by calculating the internal composite reliability (ICR) and
the average variance extracted (AVE). ICR of 0.7 and above is taken into
consideration and AVE greater than .50 is taken into consideration. In
PLS model path coefficients represent standard beta values while R2
represent the amount the variance explained. A correlation analysis
was conducted on all variables to explore the relationship between the
variables. The bivariate correlation procedure was subject to two tailed
tests of statistical significance at two different levels highly significant
(p < 0.01) and significant (p < 0.05). The result of correlation analysis
for all the variables is shown in (Table 5) (Figure 4). |
| • Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). |
| It examines the correlations among perceived usefulness, perceived
ease of use, Attitude, Behavioral Intention to Use, Assertive, Aggressive
and Passive. |
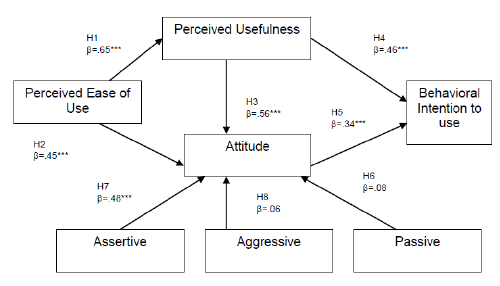
Hypothesis -1 (Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU) → Perceived
Usefulness (PU)) |
| PEOU is found to be statistically significant with PU where β =
0.65, p < 0.001, R2 = 0.34. This suggests that Physicians, perceive mobile
banking is easy to use will prove to be useful for them. The findings
suggested that, sample of Physicians who have perceived in easy
in using mobile banking perceive usefulness of mobile banking for
conducting their banking transaction or payment. |
Hypothesis -2 (Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU) → Attitude (ATT)) |
| PEOU is found to be statistically significant with ATT where
β = 0.45, p < 0.001, R2 = 0.48. This suggests Physicians attitude is
significantly affected by the perceived ease of use of mobile banking.
Another implication of this as physicians is familiar with the smart
phone devices which also forms a positive attitude towards mobile
banking. |
Hypothesis -3 (Perceived Usefulness (PU) → Attitude (ATT)) |
| PU is found to be statistically significant with ATT, where β = 0.56,
p < 0.001, R2 = 0.35. Physicians derived their usefulness from mobile
banking usage which is forming a positive attitude towards it. |
Hypothesis -4 (Perceived Usefulness (PU) → Behavioral
Intention to Use (BIU)) |
| PU is found to be statistically significant with BIU, where β = 0.46,
p < 0.001, R2 = 0.65. Usefulness of mobile banking is leading to the
intention of using mobile banking in future. It can be viewed as more
the usefulness of the users more will be the intention of using mobile
banking. |
Hypothesis -5 (Attitude (ATT) → Behavioral Intention to Use
(BIU)) |
| ATT significantly impact on the behavioral intention to use where
β = 0.34, p < 0.001, R2 = 0.45. Physicians maintain a positive attitude
towards mobile banking usage and also satisfied with ease of use and
usefulness they derive from the mobile banking. |
Hypothesis -6 (Passive Behaviour → Attitude (ATT)) |
| Passive behaviour characteristics of physicians are not having
a positive attitude towards use of mobile banking and this is not
statistically significant as per the analysis results. Passive behaviour is
not significant on attitude where β = 0.08, p > 0.001, R2 = 0.55. Aggressive
behavior people having low self esteem, lack of self confidence, lack of
self respect and negative feelings and thoughts are having a negative
attitude formation towards mobile using mobile banking. |
Hypothesis -7 (Assertive Behaviour → Attitude (ATT)) |
| Assertive behaviour characteristics of physicians are having a
positive attitude towards use of mobile banking and this is statistically
significant as per the analysis results. Assertive behaviour is significant
on attitude where β = 0.48, p < 0.001, R2 = 0.65. Aggressive behavior
people having high self esteem, high self confidence, have high self
respect and positive feelings and thoughts are having a positive attitude
formation towards mobile using. |
Hypothesis -8 (Aggressive Behaviour → Attitude (ATT)) |
| Aggressive behaviour characteristics of physicians are having a
negative attitude towards use of mobile banking and this is statistically
not significant as per the analysis results. Passive behaviour is not
significant on attitude where β = 0.06, p > 0.001, R2 = 0.15. Aggressive
behavior people having lack of self confidence, lack of self respect and
negative feelings and thoughts are having a negative attitude formation
towards mobile using mobile banking. |
Discussion and Managerial Implications |
| Banking will be using predictive behaviour model in minimizing
the risk of delivering their financial services. The research contributes
to the existing literature on mobile banking adoption among customers
with special focus on physician’s adoption. TAM model has power in
explaining the technology acceptance by users. In one eye theoretical
knowledge is enriched with practical contribution to the filed of
banking as well as health sector. It has tried to find out the factors in particular to behavior of customers. It has found how the behavioral
characteristics are affecting the attitude which in turn influences
behavioral intention to use mobile banking. |
| As per the study, behavioral characteristics play a vital role for
attitude formation. PU and PEOU, ATT are the main predictors of
technology acceptance. The hypothetical model was constructed and
validated to predict factors which affect mobile banking adoption
among physicians. The Partial Least Squares Path Modeling a variation
of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed to validate both
measurement and structural model. Furthermore, results displays
that perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, attitude, and assertive
behavior of physicians are the main predictor for the adoption of
mobile banking. |
| From the banker’s point of view, bank should promote positive
attitude towards mobile banking among customers. Mobile banking
adoption is driven by attitude and personality style of physicians.
As attitude is built among physicians then they become an effective
customer for mobile banking. Assertive behavior of physicians has the
skills to state their opinion, try to influence others while the aggressive
behavior physicians will force their opinion on others for the usage of
mobile banking. Assertive people have a better chance of gaining the
respect of those around them as they are able to stand up for themselves
while considering the needs and views of others. Aggressive people can
be unapproachable, show they don’t have positive attitude towards the
mobile banking. This significant relationship suggests that physicians
who perceive mobile banking as a useful channel for doing banking
activities more likely prefer to use it. |
| Physicians using mobile banking save time by using the service
effectively and efficiently. Physicians prefers mobile banking because
they are charged less for performing banking transaction compared
to in branch services. Additionally, customers might use mobile
banking to have greater control over their financial activities from
anywhere at any time without going to bank branches and standing in
queue. Aggressive people may show irritated manner at others while
assertive people appear relaxed in stressful situation which shows a
positive attitude for adoption of mobile banking. They have a negative
attitude and forget to carry out tasks. Assertive is the healthiest and
most effective style of communication, and have the confidence to
communicate without restoring manipulations. Different mobile
banking strategy for segment strategy. Positive assertiveness among the
physicians indicate their leadership ability, reduce conflict, Increase the
quality of the relationships both at work and in their personal life, and
to get more of what they want in life. This indicates a positive attitude
towards adoption of mobile banking. They are good communicators
to know their needs and expectations by communicating them clearly.
Customer expectations, technological innovations; effect of regulation
with attitude formation towards the technology acceptance plays a vital
role for the adoption of mobile banking. Significant influences of ease
of use on mobile banking suggest bankers that physicians will use if
they feel comfortable to operate and for them it will be easy to use.
User friendly interface, easy instruction to follow will promote the
physicians in adoption of mobile banking. |
| Bankers should focus more on this aspect while designing the
channel for distribution of financial services. More and more physicians
are inclined for use of mobile devices rather than for internet banking
due to the small devices they carry with it. From this study bank should
consider the behavioral characteristics of customers in different group
segment while designing their strategy for distribution of financial
services. In the study assertive behavior among physicians’ is much more prevalent still then many physicians even familiar with smart
devices don’t adopt mobile banking where the behavioral style of
physicians play a important role in the attitude towards adoption of
mobile banking. |
Conclusion |
| This study represented as distinctive research in the adoption
of mobile banking that integrated the behavioural style factors
with TAM model. The findings discovered the assertive behaviour
of physician’s forma positive attitude towards adoption of mobile
banking. Aggressive and passive behaviour forms negative formation
towards the behavioural intention to use mobile banking. Perceived
usefulness, perceived ease of use, assertive factors is significant in
affecting physician’s attitude which leads to the behavioral intention
to use mobile banking. Study also found attitude plays vital role in the
intention to use mobile banking or with the continued use of mobile
banking in future. Further study can be enhanced by taking into the
consideration of culture factor with the personality behavior style of
physician’s in formation of attitude towards the adoption of mobile
banking. The study was an attempt to attract a particular segment of
the society which is highly educated and occupying a noble possession
to pass message to society to create cash less society where patient,
doctor and other stakeholders in the health sector transact each other
in financial issues as well as other banking transaction. |
Tables at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Table 1 |
Table 2 |
Table 3 |
Table 4 |
Table 5 |
|
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
|
References |
- Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly 13: 319-340.
- Yang KC (2005) Exploring factors affecting the adoption of mobile commerce in Singapore. TelemInform 22: 257-277.
- Davis FD, Bagozzi RP, Warshaw PR (1989) User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science 35: 982-1003.
- Adams DA, Nelson RR, Todd PA (1992) Perceived usefulness, ease of use, and usage of information technology: A replication. MIS Quarterly 16: 227-247.
- Agarwal R, Prasad J (1999) Are individual differences Germane to the acceptance of new information technologies? Decision Sciences 30: 361-391.
- Venkatesh V (2000) Determinants of perceived ease of use: Integrating control, intrinsic motivation, and emotion into the technology acceptance model. Information System Research 11: 342-365.
- Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD (2003) User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS 27: 425-478.
- Mattila M (2003) Factors affecting the adoption of mobile banking services. Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce 8: 24-36.
- Nor KM, Pearson JM (2008)An exploratory study into the adoption of internet bankingin a developing country: Malaysia. Journal of Internet Commerce 7: 29-73.
- Ajzen I, Fishbein M (1980) Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Englewood Cliffs, Prentice-Hall.
- Davis FD, Bagozzi RP, Warshaw PR (1992) Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace. Journal of Applied Social Psychology 22: 1111-1132.
- Chau PYK, Hu PJ (2001) Information Technology Acceptance by Professionals: A Model Comparison Approach. Decision Sciences 32: 699-719.
- Agarwal R, Prasad J (1998) A conceptual and operational definition of personal innovativeness in the domain of IT. Information Systems Research 9:204-215.
- Venkatesh V, Davis FD (1996) A model of the antecedents of perceived ease of use: Development and test. Decision Sciences 27: 451-481.
- Venkatesh V, Davis FD (2000)A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: F our longitudinal field studies. Manage Sci 46: 186-204.
- Hair J, Anderson J, Norman J, Black W (1995) Multivariate Data Analysis with Readings 4th (edn.). Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
|