ISSN: 1204-5357
ISSN: 1204-5357
Galina Aleksandrovna Mashentseva*
Kamyshin Technological Institute, Volgograd State Technical University, Russian Federation
Ekaterina Ivanovna Doroshenko
Kamyshin Technological Institute, Volgograd State Technical University, Russian Federation
Elena Borisovna Goncharova
Kamyshin Technological Institute, Volgograd State Technical University, Russian Federation
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce
Within the framework of the article, a hypothesis of the existence of a statistical correlation between the level of GDP and the volume of the advertising market was offered. The foundation of the found correlation is performed by means of the correlation and regression analysis. However, the dependence revealed is not accurate statistically, and this determined the need to reveal other factors being in close correlation with the volume of the advertising market.
Advertising Market, Gross Domestic Product, Estimation of Advertising Market, Investment Attractiveness, Global Competitiveness Index, Global Human Potential Index
Within the framework of this research, the hypothesis is made that there is a close connection between the GDP and consumer expenses, and the volume of the advertising market of the country. Besides, this dependence is typical for the periods of development and also for the periods of economic instability, connected with the serious slowdown or decline of the advertising markets. But most studies of the advertising market are concentrated on the study and revealing of the interdependence only between the volume of the advertising market and gross domestic product of the country per capita. Actually, this is one of the main indicators of the development level of the advertising market. However, it is evident that GDP is not the only indicator of the development level of the advertising market.
It should be mentioned that now it is difficult to imagine the analysis of economic phenomena without applying the econometric models. Besides, the regression analysis is the most studied section of the econometric modeling and it proved itself as a rather efficient tool of solving various economic problems [1].
To study the advertising market and the degree of influence of various factors, we use the multiple correlation and regression analysis. As a result of the use of the multiple correlation and regression analysis, the analytic expression of the form of correlation between the resulting sign Y and factor signs x1, x2, x3, an is determined. Thus, the function is the following:
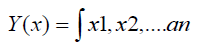 (1)
(1)
where n is a number of factor signs.
In multiple regression, the linear equation is used that looks the following:
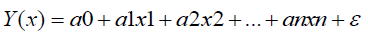 (2)
(2)
Where a0, a1, …, an are parameters of the model (coefficients of regression); ei is a random variable (value of excess).
The coefficients of regression show at what value, on the average, the resulting sign will change if the variable changes for the measurement unit at the fixed (constant) value of other factors included into the regression equation [2]. It is typical for social and economic phenomena that together with the existing factors they are influenced by many other factors including the random factors. In this regard, the existing dependence is not revealed here in every particular case as it is in the functional correlations but on the overall average in a large number of observations. In such case, it is a statistical dependence.
The result of the analysis is a calculated multiple correlation coefficient R equal 0.71 that indicates the close correlation between the volumes of the advertising market and the indices of the investment attractiveness of a region and the degree of the investment risk.
The range of problems of the study of the advertising market in a down economy is paid close attention by the academic specialists and analysts-experts. In this regard, it is necessary to pay special attention to some provisions and results of the projects that, according to the authors, should be taken into account in the further research [3].
Some scientists confirm the correlation of the advertising costs with the general economic situation in this or that market. Thus, for example, Jones detected the close (but not 100%) correlation between the level of the gross national product (GNP) and the advertising activity in the materials of 1961-1983. Other researchers, having studied 8 countries at the end of the 1990s, detected in 6 of 8 countries the statistically significant correlation of the advertising costs and the GDP. Studying the markets in the recession periods showed that between the estimations of the GDP and the advertising costs there is a light correlation in the compared prices in 6 of 9 industrially developed countries.
According to the results of some studies, companies, as a rule, decrease the budgets during the decline and increase them again when the decline is over. Discussing the influence of the situation in the economy on the advertising costs, researchers often point out the role of the mechanism of budgeting. In practice, the most widespread approach to the budget allocation for advertising is a percent from the expected/previous sales or the volume of costs that company considers “possible”. It explains partially the connection between the state of the economy and the level of advertising costs. The decrease of the advertising costs in the recession periods is often explained by the fact that the advertising costs are, to a far greater extent, subjected to the operative correction in comparison with the costs for personnel, production, realestate and equipment.
It is important that advertising costs are different in different years and countries. Having considered the general advertising costs in 43 countries in the 1970s, Banks made the following conclusions:
• A share of advertising in the GDP depends upon the economic and social development;
• On the whole, the difference in a share of advertising costs in the economy observed in particular countries and particular periods is explained mainly by the structure of the economy;
• Some branches and sectors are advertised more actively [4].
Attention should be paid also to the recent research of the famous specialist in the sphere of marketing communications Tellis that is dedicated to the study of advertising during the recession. 40 papers have been subjected to the secondary analysis where the various sides of the advertising activity were considered in the conditions of the economic instability. At the same time, the attention of the authors was focused on the four subject areas: sensibility of the advertising costs to the state of the economy; market behavior of brand and private-label products in the conditions of growth and decline of the economy; the influence of advertising on the profit of a company during the recession and after it.
Within the context of this article, in our opinion, the following generalization is the most interesting: the advertising market is rather sensitive to the cycles of changes in the economy measured by the dynamics of the GDP.
This dependence fluctuates significantly from one country to another and partially can be explained by the peculiarities of the business and the “parameters” of the culture on the whole in a particular market. In the cultures with a more long-term orientation and longer distance of the power, the advertising activity is less cyclic with respect to the fluctuations between the points of the maximal growth and maximal decline. At the same time, the biggest cyclicity of the advertising activity is observed in the countries with the highest rejection of the uncertainty (less inclination to risk). In respect to the particular segments, the sensitivity of the newspapers and magazines to the changes in the economy is significantly higher than the sensitivity of the electronic segments, i.e. television and radio.
It is evident that the studying of advertising costs in the context of the economic development is not only of theoretical interest. Even the small change in the proportions of the advertising investments in regard to the economy as a whole is expressed in the significant absolute values. It is important that even a share of advertising budgets is more or less constant, not all segments can take a constant share due to the re-distribution of the budgets among them [5].
Some researchers confirm the dependence of the advertising costs on the economic conjuncture. That means there is the interdependence between advertising costs and the general economic situation in one or another market. For example, Nikolaev et al. [6] mention in the analytic report that “One of the most convenient indicators for the estimation of the level of regional differentiation is the GRP/GDP per capita. The main advantages of this indicator are the commonality of the methods of calculations to provide the comparability and availability of the data in the long-term retrospective view, and this gives the possibility to follow the dynamics” [7]. According to the results of some studies, companies, as a rule, decrease the advertising budget during the decline and increase it again when the decline is over [8]. Discussing the impact of the situation in the economy on the advertising costs, the researchers often point out the role of the mechanism of the budgeting. Attention should also be paid to the research performed by the famous specialist in the sphere of the marketing communications Tellis that was dedicated to the study of advertising during the recession [3]. 40 studies have been subjected to the secondary analysis where the tendencies of the various sides of the advertising activity were considered in the conditions of the economic instability.
In this research, it is offered to prove the dependence between the GDP and the level of the development of the advertising market on the base of the statistic data, and also to attempt to determine the other factors influencing it.
For the purpose of the problems of this research, the most interesting, in the authors’ opinion, is the following generalization: the advertising market is very sensitive to the cylcicity of the economy measured by the dynamics of the GDP [9].
Such dependence changes significantly in different regions and partially can be stipulated by the peculiarities of the organization and conduction of business in the region and the “parameters” of the culture of a particular market. Cultures that are directed to the long-term orientation and have a large distance of power are characterized by less cyclic advertising activity from the point of view of the fluctuations between the points of maximal growth and maximal decline. At the same time, the countries with the significant rejection of uncertainty (less inclination to risk) are characterized by the biggest cyclicity of the advertising activity) [6].
Thus, the study of advertising costs in the interaction with the economic development is not only of theoretical interest but also practical. The synergetic effect is that relatively insignificant change in the economy is expressed in the more significant absolute values of investments into the advertising. It should be taken into account that even if a share of the budgets for advertising is rather constant not all the region can pretend for the constant share due to the redistribution of budgets among them [10].
It should be mentioned that the use of economic models is a more acceptable, efficient and non-expensive method of analysis of the economic phenomena and system. In particular, the regression analysis being the most studied section of the econometric modeling proved itself as a rather efficient tool when solving various economic problems [8].
Let us estimate the European advertising market characterizing the dependence of the change of volume of the advertising market of the country [11] depending upon the volume of the GDP [12]. As a result, the following obtained data are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Regression analysis “GDP- European advertising market”, the authors’ development.
| Multiple R | 0.60999 |
| R-square | 0.372087 |
| Observations | 20 |
| F | 10.66641 |
| Coefficients | |
| Y-intersection | -1472.82 |
| Variable X 1 | 2008.411 |
Using the F-test, we can check the signification of the regression equation. At the design value (Fdesign) equal to 10.66, the table value of the criterion with the confidence probability 0.95 and a number of degrees of freedom γ1 = k = 1 and γ2 = n-k-1 = 20-1-1 = 18 equals to 2.1. As Fdesign > Ftable, the regression equation is considered acceptable. The multiple coefficient of correlation R is equal to 0.61, which allows to conclude about the existing connection between the level of the GDP and the volume of European advertising market. The obtained value of the multiple coefficient of determination Rsquare 0.4 shows that the existing 40% of the variation of the dependent variable (the volume of the advertising market) are stipulated by the factor – volume of the GDP, and 60% – by the factors not included in the model.
According to the data of 2013, such dependence of the volume of European advertising market on the volume of the GDP is the following:
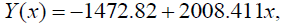 (3)
(3)
where Y(x) is a resulting indicator – the volume of the advertising market, dollars per capita; x is a factor – the volume of GDP, dollars per capita.
The regression coefficient a1 = 2008.411 points out that the increase of the GDP at 1 dollar per capita leads to the growth of the volume of the European advertising market by 2008.411 dollars per capita [13].
The authors believe that the estimation technology of the level of development of the markets that presupposed its connection to the volumes of the GDP of the country does not allow to follow the dynamics of development of the advertising markets completely from the point of view of effectual demand for the advertising services, especially in the conditions of the market globalization, saturation of the advertising market and aggressive competitiveness. Due to this, the use of integral indicators that take into account the regional aspect becomes more important [14].
The non-uniform development of various regions of the world leads to the intensification of the differentiation of the advertising markets. The investment-attractive spheres of business include the perspective types bringing profit from investments and having a fast payback period, and they are also characterized by the high values of profitability and low level of risk. In such a case, the regions perform as economic entities and compete for the advertising investments of the largest advertisers of the world [15]. As a result of the competitive struggle, the regions possessing the high competitive advantages in comparison with the others win. The most perspective and investment attractive regions acquire the monopolistic power to attract advertising investments into its economy. As a result, the spacial monopoly is formed; that is the situation where a particular sphere of the national economy is focused within the frameworks of one regional economic system.
As a result, in the corresponding conditions of the development, the spacial monopolies become centres where the particular resources and the sources of the economic growth are concentrated. And the higher level and degree of the economic development of the region, the more competitive it is, and, consequently, it is more attractive for the investments into the advertising business [16].
From the above stated we can conclude about the connection of the GDP of the volumes of regional advertising markets. But now it is evident to reveal the factors that stipulate 60% of the changes in the volumes of the advertising markets, that is, those factors that were not taken into account in the model above. The factors that the authors offer to consider are the indicators of the investment attractiveness of the region:
1. Global Index of Human Development [17];
2. Global Competitiveness Index [18].
The result of the regression analysis is the following: the multiple coefficient of correlation R is equal to 0.71; that means that there is a close connection between the volumes of advertising and indices that are included into the model. The data are shown in Table 2.
The model of the dependence of the volumes of advertising markets and global indices in 2013 is the following:
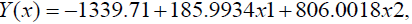 (4)
(4)
Where Y(x) is a resulting indicator – the volume of the advertising market, dollars per capita; x1 is the first factor – global competitiveness index; x2 is the second factor – global index of human potential.
Table 2: Regression analysis of the advertising markets taking into account their investment attractiveness, the authors’ development.
| Multiple R | 0.716335 |
| Observations | 20 |
| Regression | 2 |
| Excess | 17 |
| F | 8.95866 |
| Coefficients | |
| Y-intersection | -1339.71 |
| Variable X 1 | 185.9934 |
| Variable X 2 | 806.0018 |
The result of the analysis performed is the clusterization of the European advertising market into three segments [19]. Let us consider the clusterization of the European advertising market in Figure 1.
Within the framework of this article, the correlation connection between the volume of the advertising market and the level of GDP was confirmed. The obtained dependence determined the necessity of the further revealing of factors, the inclusion of which intocorrelation and regression model would allow to increase its significance greatly and, consequently, to improve the accuracy of this model [20]. In the opinion of the authors, the indicators of the investment attractiveness of the region can be the following factors: the competitiveness index and the human potential index. Further research within the framework of this hypothesis can be connected to the attempt to determine the factors that will increase the statistical significance of the revealed model.
Copyright © 2025 Research and Reviews, All Rights Reserved